A Comprehensive Guide How to Stop Prostate Enlargement
Introduction
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), commonly referred to as prostate enlargement, is a common condition that many men experience as they age. Prostate enlargement is a normal aspect of aging, but it can be managed and even prevented with early detection. This thorough guide will Cover the causes, symptoms, and Most importantly effective ways how to stop prostate enlargement.
Understanding How To Stop Prostate Enlargement
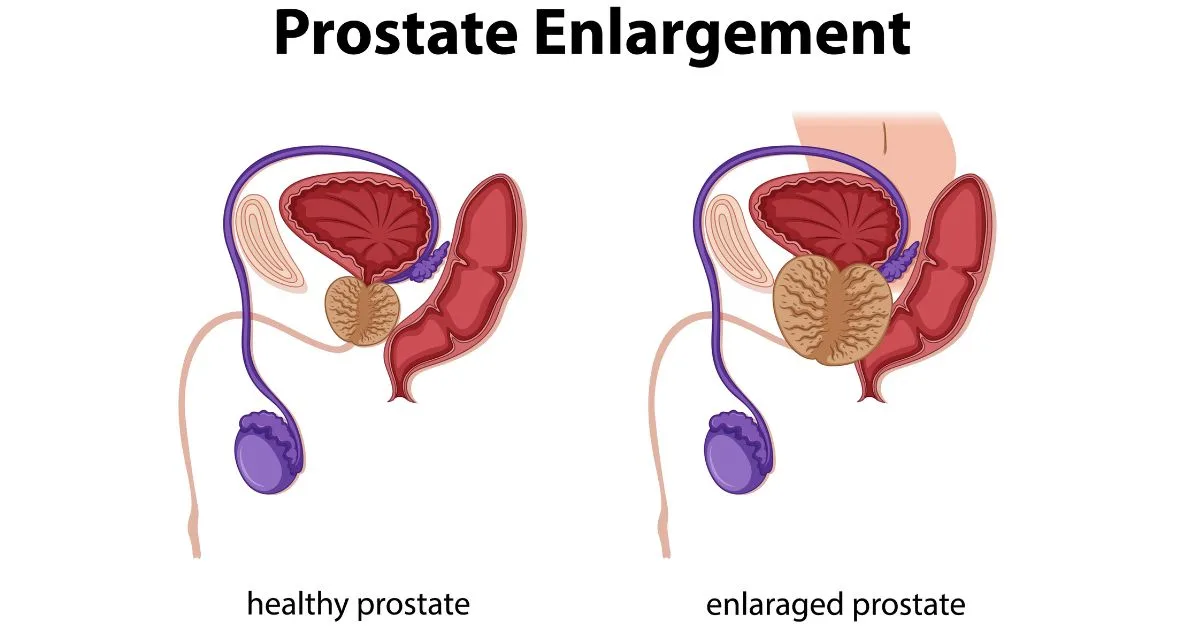
The prostate is a small gland situated in front of the rectum and beneath the bladder. Producing fluid to nourish and transport sperm is its main job. BPH is frequently caused by a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate in men as they age. Although there is no risk to life, this condition can cause unpleasant signs like frequent urination, difficulty initiating and maintaining an ongoing flow, and a feeling that the bladder is not completely empty.
Causes Of Prostate Enlargement
Prostate enlargement develops as a result of multiple factors. It is essential to understand these elements in order to put into practice efficient preventive measures. Among the main contributors are:
Hormonal Changes: Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) excess, in particular, is a major factor contributing to prostate enlargement due to changes in the hormonal balance. As an outcome of testosterone, DHT is thought to promote the growth of prostate cells.
Age: The risk factor for prostate enlargement that cannot be changed is age. An enlarged prostate is more likely to develop in men as they get older.
Genetics: Prostate enlargement is influenced by family history as well. You may feel more vulnerable if any close relatives have had BPH.
Lifestyle Factors: Studies have shown a link between an elevated risk of prostate enlargement and sedentary lifestyles, poor diets, and obesity. Prostate health can be increased by living a healthy lifestyle.
Preventive Steps to Stop Prostate Growth
Now that we know the causes of prostate enlargement, let’s discuss practical preventive strategies to stop the disease’s development:
Maintaining a Nutritional Diet:
a. Increase Your Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Eating a diet high in fruits and vegetables gives your prostate the vital nutrients and antioxidants it needs to function properly.
b. Select Healthy Fats: Go for fats that are good for you, like those in avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish. These fats function as anti-inflammatory agents.
Stay Active:
a. Exercise Frequently: Research has indicated that regular exercise lowers the risk of prostate enlargement. should try to do at least 150 minutes exercise in a weak.
Manage Stress:
a. Use Stress-Reduction Methods: Prostate health can be adversely affected by ongoing stress. Include stress-relieving techniques in your routine, such as yoga, deep breathing, or meditation.
Sustain a Healthy Weight:
a. Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Prostate enlargement is more common in obese people. It can be advantageous to reach a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Supplements for a Healthy Prostate:
a. Examine Natural Supplements: Saw palmetto and beta-sitosterol are two supplements that have demonstrated potential in aiding prostate health. Before introducing supplements into your diet, speak with your physician.
Routine Prostate Examinations:
a. Arrange for Frequent Checkups: Prostate screenings on a regular basis are essential for early detection and treatment. Talk to your doctor about which screening tests are appropriate for your age group.
Medication Options:
a. consult with Your Doctor: Medication may be recommended in certain circumstances to control symptoms and halt the growth of prostate enlargement. You should always speak with your doctor before beginning any new medication.
Additional Common Questions
Is An Enlarged Prostate Serious?
While BPH is not considered to be a life-threatening condition in and of itself, untreated BPH can lead to complications. Possible issues consist of:
Acute Urinary Retention: The sudden inability to urinate is known as acute urinary retention, and it can be a medical emergency that needs to be attended to right away.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Because BPH causes incomplete bladder emptying, there is a higher chance of developing UTIs.
Bladder stones: Minerals can accumulate in the bladder after a prolonged amount of urine is retained.
Kidney damage: Prolonged severe BPH episodes may cause renal damage.
The degree of symptoms and how they affect your quality of life will determine the best course of action for treating an enlarged prostate. Among the treatment options are medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical procedures.
Can An Enlarged Prostate Go Back To Normal?
Numerous therapies are available to help control symptoms and, in certain situations, shrink the prostate.
Medication: A doctor may prescribe specific drugs to treat the symptoms of BPH. Prostate gland shrinkage and muscle relaxation are common uses for alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, respectively.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: By shrinking the prostate, minimally invasive techniques such as laser therapy and transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) can help relieve symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes: A change in lifestyle may help alleviate symptoms. Examples of these adjustments include cutting back on alcohol and caffeine, controlling hydration, and engaging in pelvic floor exercises.
Surgery: When other treatments are not working or the condition is more severe, a prostatectomy or other surgical procedure may be advised to remove part or all of the prostate.
Can Prostate Be Cured Without Surgery?
Here are some common non-surgical treatments for conditions relating to the prostate:
Active Surveillance: Active surveillance is a potential treatment option for certain cases of prostate cancer, particularly those with low-risk characteristics. This involves closely monitoring the cancer without starting treatment right away. If there are signs that the disease is progressing, treatment may be started.
Radiation therapy: To target and destroy cancer cells, high-dose radiation is used in radiation therapy. When used as the main course of treatment or in conjunction with surgery, it can be a successful treatment for prostate cancer.
Hormone therapy: Male hormones like testosterone are frequently the driving force behind prostate cancer. The goal of hormone therapy is to lower these hormone levels or prevent them from having an impact on cancerous cells.
Cryotherapy: Prostate tissue is frozen during cryotherapy in order to eliminate cancerous cells. It is a less invasive alternative to surgery that might be taken into account in specific situations.
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU): This non-surgical procedure heats and kills prostate tissue, including cancerous cells, using ultrasound waves.
Chemotherapy: Although it is not as frequently used for prostate cancer as it is for some other forms of the disease, it may be suggested in some circumstances, when the cancer is spread outside the prostate.
Enlarged Prostate Diet
The following general dietary guidelines might be helpful:
Produce and Fruits: Consume variety of fruits and vegetables because they are high in vitamins and antioxidants. Prostate health may be supported by these nutrients.
Fiber: Eat a diet rich in whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, as well as other high-fiber foods. Constipation can be avoided and bowel movements can be regulated with the aid of fiber, which may be good for prostate health.
Good Fats: Select healthy fats, like those in avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish (like salmon). Particularly omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory qualities.
Cut Back on Trans and Saturated Fats: Limit your consumption of red meat, processed foods, and fried foods, which are high in saturated and trans fats. Consuming these fats in excess may exacerbate inflammation.
Tomato Products and Tomatoes: According to certain research, lycopene, which is present in tomatoes and tomato-based products, may protect the prostate. Cooking tomatoes causes them to release more lycopene, so think about eating foods that contain tomatoes.
Green Tea: Antioxidants found in green tea may have anti-inflammatory effects. It’s a healthy beverage option all around.
Limit alcohol and caffeine: Alcohol and caffeine should be avoided as they can aggravate bladder irritation and the symptoms of an enlarged prostate.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water to ensure that you are properly hydrated, drink lots of water. Maintaining urinary function and general health depend on adequate hydration.
Moderate Consumption of Calcium: Higher risk of prostate cancer has been linked to elevated calcium levels. Go for a moderate amount of calcium and think about getting your calcium from food rather than supplements.
Limit Consumption of Sodium: Cutting back on sodium consumption may improve general health and help control blood pressure. Prostate symptoms may worsen due to high blood pressure.